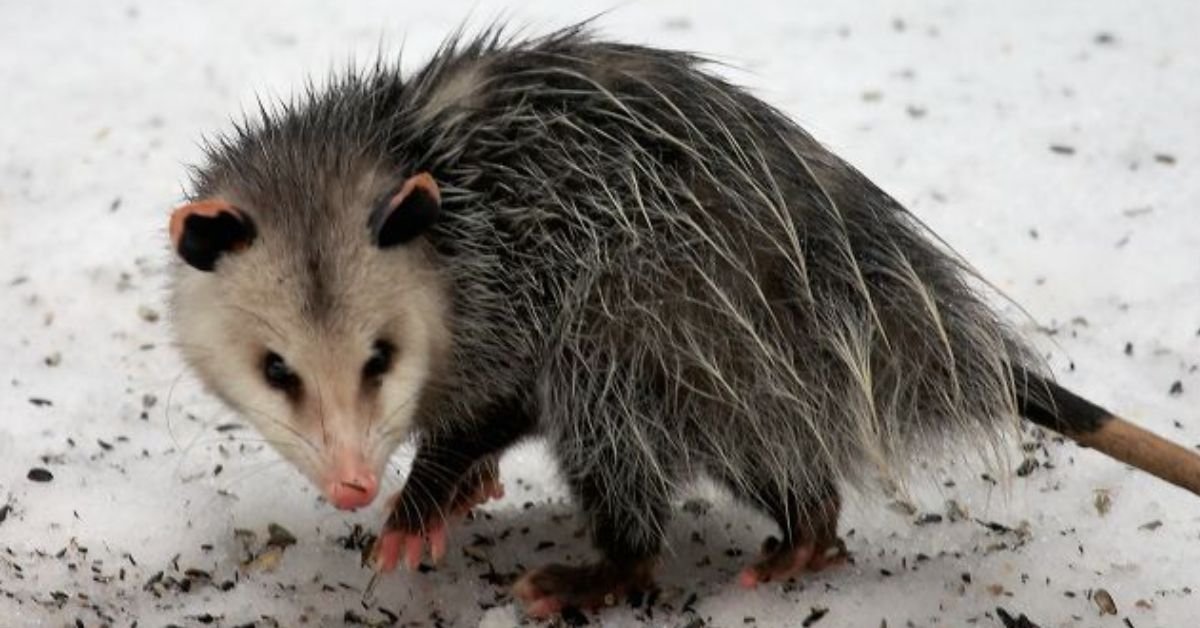
The tñacuache, often called the Mexican opossum, is a nocturnal creature with remarkable survival skills. Found throughout Mexico, Central America, and parts of the southern United States, this marsupial is often misunderstood yet plays a crucial role in its ecosystem. This article delves into the behaviour, survival strategies, and unique characteristics of the tñacuache, shedding light on why it’s such a fascinating animal.
Understanding the Tñacuache: The Basics
Before diving into its behaviour and survival mechanisms, it’s essential to understand what a tñacuache is. This nocturnal marsupial belongs to the family Didelphidae and is closely related to the opossum found in North America. The tñacuache is unique because it is native to Mexico, Central America, and parts of the southern United States, where it thrives in diverse environments.
Physical Characteristics of the Tñacuache
The tñacuache is typically about 40-50 cm long, with a long prehensile tail that helps it maintain balance and manoeuvre through trees. It has a pointed snout, large round ears, and sharp claws, all of which make it an excellent climber and scavenger.
The Behavior of the Tñacuache: Nighttime Wanderer
The tñacuache is primarily nocturnal, meaning it is most active during the night. It has adapted to a life that revolves around foraging for food, finding shelter, and avoiding predators under the cover of darkness.
Feeding Habits and Diet
The tñacuache is an omnivore, meaning it eats both plants and animals. Its diet includes fruits, insects, small animals, and even eggs. It’s known to forage through garbage or raid crops for food. The tñacuache’s adaptability in its diet allows it to survive in various environments, including urban and rural areas.
Social Behavior and Habitats
While generally solitary, the tñacuache will sometimes form temporary social groups, especially when there is a plentiful food source. They prefer to live in hollow trees, abandoned burrows, or anywhere that offers shelter from predators. Due to their ability to adapt to different environments, they can thrive in urban areas.
Survival Strategies of the Tñacuache
The tñacuache is known for its adaptability and unique survival techniques, which allow it to outlast predators and harsh environmental conditions.
Playing Dead: A Last Resort
One of the most famous defence mechanisms of the tñacuache is its ability to play dead, or “playing possum.” When threatened, it will collapse and secrete a foul-smelling liquid from its anal glands to deter predators. This makes it appear unappetizing, thus allowing it to escape danger. This survival tactic can be a lifesaver in moments of peril.
Climbing Skills and Escaping Threats
Given its excellent climbing abilities, the tñacuache can escape threats by quickly scaling trees or other high surfaces. It uses its prehensile tail to grip and balance while navigating through treetops or across uneven terrain.
The Role of the Tñacuache in the Ecosystem
Though often regarded as a nuisance due to its habit of rummaging through trash, the tñacuache plays a vital role in maintaining the balance of its ecosystem.
Pest Control and Seed Dispersal
As an omnivore, the tñacuache helps control insect populations and prevent them from becoming overwhelming. It also contributes to seed dispersal, as the fruits and plants it eats often pass through its digestive system and sprout in new locations. This helps foster new plant growth and supports the area’s biodiversity.
Cleaning the Environment
By scavenging food waste, the tñacuache plays a role similar to that of a natural cleanup crew. Its foraging habits help break down organic matter, recycling nutrients into the soil, which is crucial for maintaining a healthy environment.
FAQs about the Tñacuache
What is a tñacuache’s primary diet?
The tñacuache is an omnivore, consuming various foods, including fruits, small animals, insects, and eggs.
Are tñacuaches dangerous to humans?
No, tñacuaches are not typically dangerous to humans. They are more likely to flee than confront. However, avoiding touching them is essential, as they may carry diseases like wild animals.
Why do tñacuaches play dead?
When threatened, a tñacuache may “play dead” to avoid being eaten. This defence mechanism makes it appear distasteful to predators, giving it a chance to escape.
Can a tñacuache live in an urban area?
Yes, tñacuaches are highly adaptable and thrive in urban environments, where they forage through garbage or abandoned structures.
How long do tñacuaches live?
In the wild, tñacuaches typically live 2 to 4 years, though their lifespan can be shorter due to predation and other threats.
Are tñacuaches protected in Mexico?
In some regions of Mexico, tñacuaches are protected due to their ecological role. However, they are not universally classified as endangered.
Conclusion
The tñacuache may often go unnoticed, but its behaviour, survival strategies, and essential role in the ecosystem make it a fascinating creature to study. From its unique ability to play dead to its crucial function in pest control and seed dispersal, the tñacuache is a survivor and a vital part of the natural world. By better understanding these incredible animals, we can learn to appreciate their contributions to biodiversity and ensure their continued survival in a rapidly changing world.
Latest Post!
- Findutbes: Everything You Need to Know
- A Guide to Stem Cell IV Therapy: Uses, Benefits, and Risks
- Dealasty: Revolutionizing the Way We Shop Online
- Arcangel Height: How Tall Is the Latin Music Superstar?
- Malia Manocherian: A Journey of Inspiration and Success
- Tñacuache: An Insight into Its Behavior and Survival