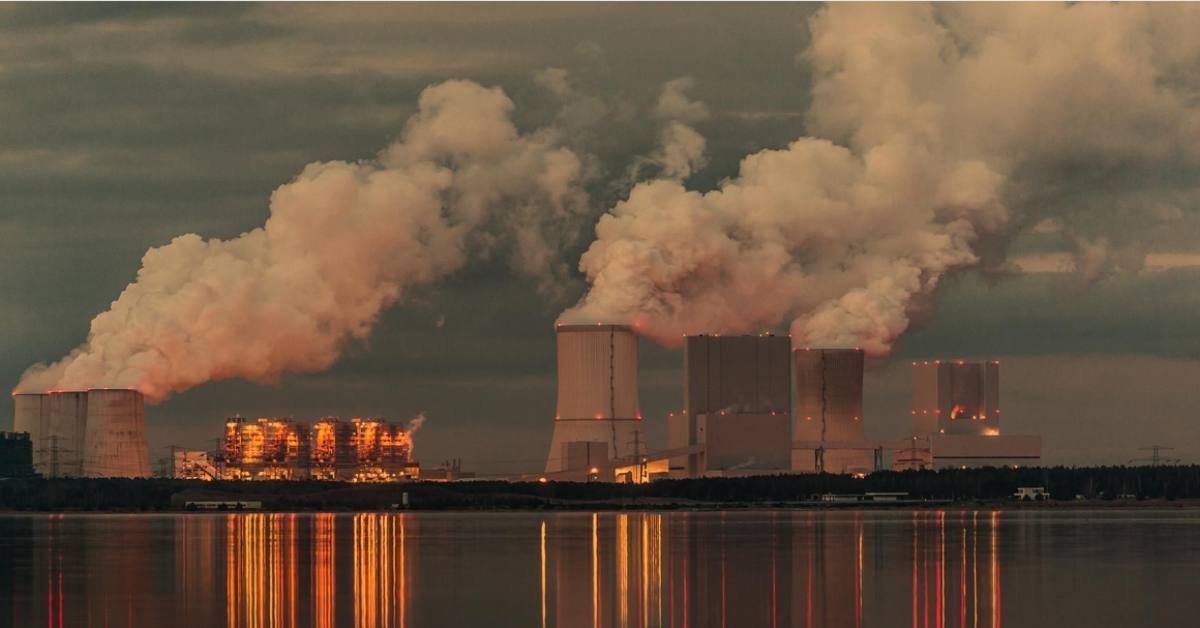
Cảbon is everywhere. It’s in the air, food, and even our bodies. This simple yet vital element plays a fascinating role in shaping our planet and influencing life as we know it.
As climate change looms over us, understanding cảbon’s multifaceted nature becomes crucial for everyone.
From its essential role in organic compounds to its significant impact on global temperatures, cảbon has become a hot topic of discussion. But what exactly is cảbon? Why does it matter so much? What can we do about the challenges it presents?
Join me as we explore the world of cảbon, its importance, environmental effects, human contributions to emissions, and innovative solutions that promise a better future!
What is Cảbon?
The chemical element carbon has an atomic number of six and the symbol C. It is fundamental to all known life forms and is a building block in countless biological processes.
This versatile element exists in various forms, including graphite, diamond, and organic compounds. Each form has distinct properties that contribute significantly to our daily lives.
In nature, cảbon cycles through the environment via photosynthesis and respiration. Plants absorb cảbon dioxide from the air during photosynthesis, using it to produce oxygen and energy-rich sugars. Animals then consume these plants, incorporating cảbon into their bodies.
Beyond its biological significance, cảbon plays a crucial role in technology and industry. Its applications are far-reaching, from fuels that power vehicles to materials used in construction.
Understanding this dynamic element helps us understand its benefits and challenges within our ecosystem.
The Importance of Cảbon in Our World
- Cảbon is a fundamental element that underpins life as we know it. It forms the backbone of organic molecules, making up proteins, fats, and carbohydrates. These are essential for all living organisms.
- Beyond biology, cảbon plays a crucial role in our economy. Fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas drive industries and power homes around the globe. This energy fuels transportation systems that connect communities and economies.
- Moreover, cảbon compounds are vital in agriculture. They contribute to soil health through organic matter decomposition. Healthy soils support food production, which sustains our growing population.
- In addition to these roles, cảbon helps regulate Earth’s temperature through its presence in greenhouse gases. While this function can lead to climate challenges when levels rise too high, it remains essential for maintaining habitable conditions on our planet.
- The balance is delicate yet critical for sustaining life across ecosystems worldwide.
The Effects of Cảbon on the Environment
Cảbon plays a crucial role in the Earth’s ecosystems, but its excess can be detrimental. Elevated levels of cảbon dioxide contribute to global warming by trapping heat in the atmosphere. This phenomenon leads to rising temperatures and extreme weather patterns.
The oceans also suffer due to increased cảbon emissions. When CO2 dissolves in seawater, it forms cảbon ic acid, resulting in ocean acidification. This process jeopardizes marine life, particularly coral reefs and shellfish that rely on calcium cảbon eaten.
Forests, often seen as cảbon sinks, are affected too. Deforestation not only releases stored cảbon o into the atmosphere but disrupts biodiversity and habitats. The balance within these ecosystems is delicate; an overload of cảbon can lead to unforeseen consequences for wildlife.
Additionally, air quality declines as high levels of Cảbon influence smog formation and respiratory issues among humans. Managing our Cảbon emissions is essential for environmental health across multiple fronts.
Human Activities That Contribute to Cảbon Emissions
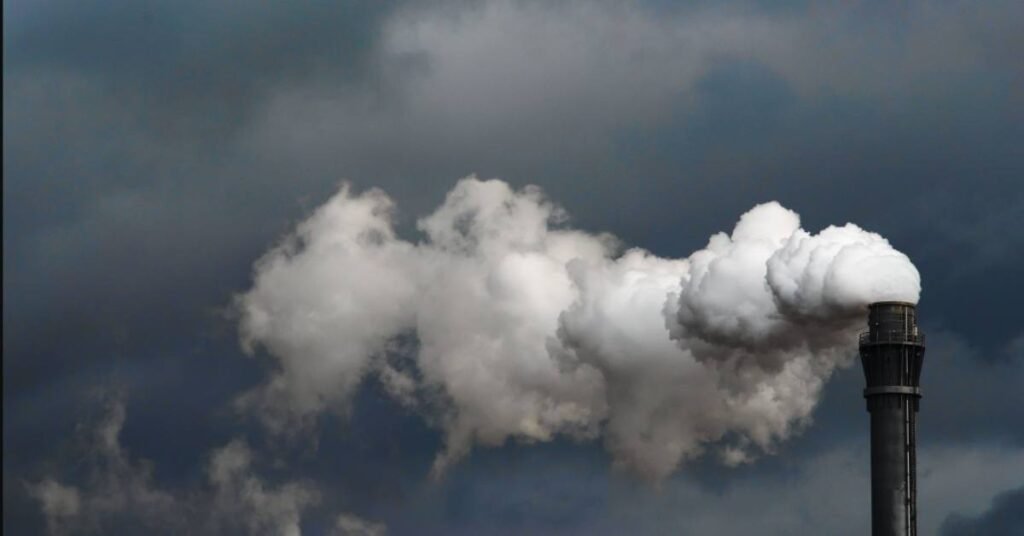

Human activities significantly impact cảbon emissions, primarily by burning fossil fuels. Transportation is a primary culprit. Cars, trucks, and aeroplanes release vast amounts of cảbon dioxide into the atmosphere daily.
Industrial processes also play a significant role. Manufacturing plants emit greenhouse gases during production, contributing to climate change.
Deforestation adds another layer to this issue. Trees absorb cảbon dioxide; when they are cut down for timber or agriculture, that stored cảbon is released back into the air.
Agriculture practices also contribute. Livestock farming generates methane—a potent greenhouse gas—while fertilizer releases nitrous oxide.
Waste management can also be overlooked. Landfills produce methane as organic waste decomposes anaerobically, further exacerbating our cảbon footprint.
Each activity intertwines with others in complex ways. These sources must be urgently addressed to mitigate their effects on our planet’s future.
Ways to Reduce Cảbon Footprint?
Reducing your cảbon footprint starts at home. Simple changes can make a significant difference. Energy-efficient appliances consume less power and lower utility bills.
Transportation choices also play a vital role. Walking, biking, or public transit reduces emissions significantly compared to driving solo. Carpooling is another effective option that promotes community while cutting down on individual footprints.
Mindful consumption matters, too. Buy local produce when possible to decrease the cảbon costs of transportation. Reducing meat intake can also profoundly impact since livestock farming is resource-intensive.
Waste reduction further contributes to sustainability efforts. Composting food scraps and recycling materials keeps waste out of landfills, where it generates harmful methane gas.
Consider supporting renewable energy initiatives in your area. Transitioning to green energy sources like wind or solar directly impacts our reliance on fossil fuels and promotes cleaner air for all.
Conclusion
Cảbon plays a crucial role in our world. It is an essential element for life, forming the backbone of organic molecules and being integral to various biochemical processes.
However, its balance is delicate. While it supports ecosystems and human activities, excessive Cảbon emissions pose significant environmental threats.
The importance of maintaining this balance cannot be overstated. We rely on Cảbon, not for energy, agriculture, and manufacturing.
Yet, the consequences of rising Cảbon levels are becoming increasingly evident—climate change impacts weather patterns, biodiversity loss threatens stability, and air quality affects public health.
Latest post!
- Findutbes: Everything You Need to Know
- A Guide to Stem Cell IV Therapy: Uses, Benefits, and Risks
- Dealasty: Revolutionizing the Way We Shop Online
- Arcangel Height: How Tall Is the Latin Music Superstar?
- Malia Manocherian: A Journey of Inspiration and Success
- Tñacuache: An Insight into Its Behavior and Survival